September 2022 Composites Blog
September 14, 2022
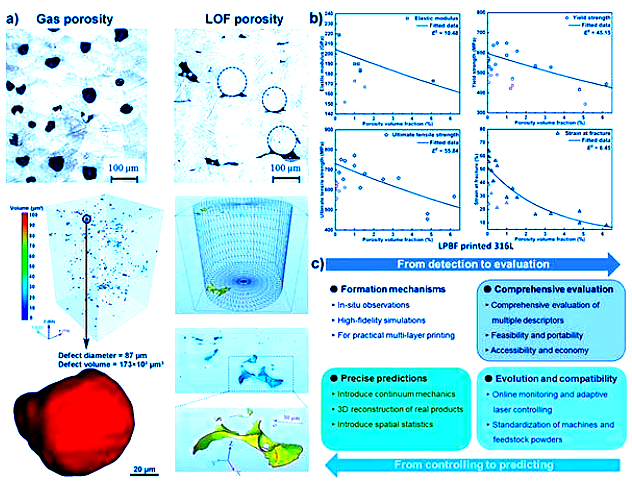
Porosity in Metals Manufactured Using 3D Printing Technologies
3D printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing (AM), is a new rising star in manufacturing technology. 3D printing is known for overcoming geometric constraints and being able to build products directly for digital models. Compared to traditional subtractive and formative manufacturing, additive manufacturing differs in that materials are added up during processing and many materials such as metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites can be manufactured using AM. A novel branch of laser engineering known as laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is a powder-based AM technology. This novel technology makes it possible to shape various metallic materials with excellent accuracy and quality making it a hot target for intense research. However, porosity and other defects are a common concern observed in LPBF printed metal products. Read more here
September 30, 2022
Creating high-performance nanocomposites using nano-dispersion approach
Today, metal nanocomposites are increasingly prominent in almost every industry. This is not surprising given their intriguing chemical and physical attributes. Metal nanocomposites are made by synthesizing metal nanoparticles with ceramics, glass, and polymeric materials. The simplest process to create them is known as the "wet chemical approach". This process has the added benefit of being cost-effective and cytocompatible, further increasing the adoption and interest in metal nanocomposites. But every ingenious invention has its challenges and while metal nanocomposites are praised for their strength, they also present notable predicaments such as minimal work hardening and poor temperature resistance which restricts their operational usefulness and causes early failure. This is why researchers in the composites field have been experimenting with a nano dispersion -in-nanograins approach which stabilizes and reinforces copper and nickel nanocomposites. Learn more here